You can also be interested in these:
- JEDEC: What is it and what is it used for?
- What is Microbenchmarking and when does it apply?
- What printer requires the less ink?
- The history of RPG and why it is beloved by many
Humans are always looking for ways to improve workflows and save time. Industrial IoT addresses those needs by connecting devices to the network, allowing data to be shared and processed with systems not connected to the factory floor.
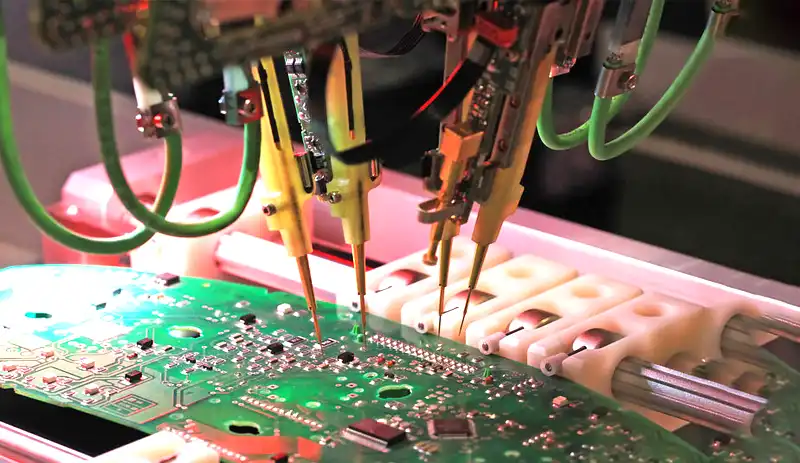
Industrial IoT provides a data-driven approach for managing industrial processes, enabling businesses to store and manage their products in real time. It also provides a way to monitor and control machinery remotely, which can decrease downtime, increase production output, improve quality control, and ultimately give the consumer an increased value-add to their chosen product. Here are some ways in which industrial IoT can optimize workflow.
1. Automation through AI
By leveraging the power of analytics, organizations can use Industrial IoT to predict product defects and improve their production capabilities. Industrial IoT is also used to analyze different manufacturing processes’ outcomes and then execute them based on the results.
By connecting machinery to a digital network, businesses can track their products using the data collected from their devices. Many of these devices can produce data on their own, but they will also give off data that other machines or systems in the factory need.
2. Enhancing security and visibility
Industrial IoT can improve security by monitoring devices and controlling access in real-time. It also provides a means for businesses to create rules and policies for each of their connected products, allowing them to monitor locations and ensure no one is tampering with them. This article shows how to build security with Industrial IoT and produce a reliable and secure network that won’t compromise your customers’ experience.
This decreases threats that could compromise product quality or safety and ensures compliance with safety standards. The increased visibility allows manufacturers to monitor how different teams perform throughout the production cycle, pinpoint any issues that could arise earlier in the process, and rectify them before they become significant problems.
3. Optimizing inventory management
IoT allows businesses to balance their supply and demand and anticipate capacity issues. For example, suppose a factory is struggling to meet the growing demands of its customers. In that case, they can use the data collected by their connected devices to detect any potential problems before they occur.
They can also identify any discrepancies in inventory that might not be visible by manually monitoring them. Having an IoT system in place allows manufacturers to find trends that are not immediately visible to humans, which helps them make informed decisions about their product lines with minimal effort.

4. Predictive maintenance for zero factory downtime
Another way in which Industrial IoT can improve process efficiency is by increasing productivity. As processes become more automated, companies have the opportunity to increase their output and make more products with minimal loss in quality.
Through predictive maintenance, Industrial IoT can monitor processes and give an alert if one of their connected products is about to malfunction. According to a recent study, Industrial IoT can detect 30–90% of issues before they occur.
5. The circular economy and lean manufacturing
By encouraging the use of resources, Industrial IoT can help companies save money and make better-informed decisions regarding their manufacturing processes. The circular economy provides a way to reuse the materials that are not essential in each production stage while also ensuring they are responsibly disposed of at the end of a product’s life cycle.
This helps manufacturers reduce their costs and also take better care in using energy by using green energy sources rather than fossil fuels. It also helps to lessen their footprint on the environment. The circular economy also encourages using sustainable materials, reducing the risk of pollution and creating healthier environments for future generations.
For instance, industrial IoT can detect when devices need to be replaced or repaired due to age, ensuring they are adequately maintained to ensure the longevity of their operation. This helps manufacturers reduce waste and also reduces their costs in replacing parts.
6. Device management and configuration management
Device management provides a way to track the physical location of devices while also keeping control over their maintenance and configuration. It also allows manufacturers to access additional data, such as sensor output and information regarding environmental conditions.
It also supports the creation of new policies and the implementation of regulations for connected products. Combining all this data allows manufacturers to make more informed decisions about which products are safe for their environment and how they can best care for them, making it easier to implement circular economy principles in their manufacturing processes.
7. Remote management and monitoring
Remote management allows manufacturers to maintain their products remotely by connecting them to the network. This will enable them to keep track of critical attributes of the devices, such as their location and operation status.
It also allows businesses to understand an asset’s history, including where it has been maintained, its previous condition, and how it has been used over time. This information is crucial in making better-informed decisions about the longevity of an asset and ensures they can meet any regulatory requirements based on their business goals.
Using the Industrial Internet of Things to monitor operational performance, factories can reduce waste and improve product quality. It can also help participants catch unexpected issues and prevent them from becoming major problems in their operations.
By linking up their equipment, companies can manufacture products simultaneously, which allows them to produce more with a minimal loss in quality. This equates to increased productivity and production efficiency, which is crucial for manufacturers trying to thrive in a competitive market.
More stories like this
- JEDEC: What is it and what is it used for?
- What is Microbenchmarking and when does it apply?
- What printer requires the less ink?
- The history of RPG and why it is beloved by many
- What is Dark Silicon and what is it currently used for?
- How to protect smartphones against Pegasus virus