You can also be interested in these:
- H264 vs AV1 vs H265: What is the best video CODEC?
- How to connect two TVs together using a single source
- What are the most used output ports in modern video cards?
- How do I know if my computer can run 4K resolution
One of the main disadvantages when working with multimedia files, especially video, is the resulting weight of the files and the storage capacity. Over time we have had compression formats that have solved this problem in some part. However, when we use any compression format to make our video projects more manageable, we somehow sacrifice the final quality of the video. Lately, with the appearance of the 4K format, and those of even higher resolution, it is becoming more and more challenging to meet the demand for such high pixel requirements. Taking two of the most used compression formats, let’s see what is the difference h264 vs h265. What is the best video codec for better compression without a significant quality sacrifice.

The reason why these types of formats arise is to alleviate the burden of the files weight. Today’s internet makes extensive use of media files, and bandwidth has always been a determining factor in this. The transfer of data, combined with the high resolutions of today’s screens, demand stricter compression formats, with less loss of resolution.
Platforms like YouTube store different versions of the same video in various resolutions to serve the video that best fits the data transfer parameters. This is one way to approach the problem with a creative solution. Even so, having the most optimal compression format means to these streaming platforms greater flexibility and better results in their user experience.
The H264 MPEG-4 format
The h264 video codec, better known as MPEG-4 or AVC1 (Advanced Video Coding) has been with us since 2003. It is the video compression format that has had the most widespread use over time. By September 2019, 91% of all developers in the video industry preferred this format. Its creation proposed to solve the problem of finding a video format that significantly reduces the bitrate with good video quality. The h264 is based on the block segmentation functionality. Moreover, this format performs a series of calculations and using a prediction system eliminates the complexity and duplication of the data contained in the original video.
In its introduction it was reported that H264 gave the same Digital Satellite TV quality as MPEG-2 with a comparative bitrate saving of more than 50%. This was a considerable improvement and the reason why it is still one of the most used compression formats to this day. This compression format is also flexible enough to be applied in online broadcasting and video streaming services. It offers unmatched reliability in both low-bitrate and high-bitrate, used by many industries for an equality vast amount of devices.
The H265 HEVC format
Also known as MPEG-H or HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding) the H265 compression format was created to be the successor to H264, as a more advanced codec with an improved and more complex processing algorithm and impressive results. It was adopted as a video standard in 2013 offering a compression capacity between 25 and 50% greater than its previous version.
The H265 is the proposal of video compression formats for the new generations of display and digital media transmission. This format has the ability to maintain the bitrate of the H64 format with almost double its compression capacity and UHD HDR with a wider color gamut.
The concept behind its operation
How is it possible to obtain such a high compression capacity with such an acceptable loss? The answer, as we mentioned earlier, is in the H264 and H265 block segmentation functionality pattern. To understand the way these codecs work, we must first know how a video works. A video is nothing more than a succession of images. If we talk about a 4K video with 30fps, it is the same as to say a succession of 30 images per second of video, where each image has a size of 3840 x 2160 pixels.
In a nutshell, There is a complex array of calculations behind the functionality of the codecs. The way these work is by comparing each pair of consecutive frames within the sequence in the video. The algorithm draws a grid or coordinate system and identifies those regions or segments of the frame that show changes compared to the previous one. It also identifies which segments do not undergo any modification. With this comparison, the codec consolidates or unifies that image data that is repeated between two frames, and keeps the information that changes.
This technology, as we can conclude by judging its widespread use, has revolutionized the video production industry. The predictive system and block format are not everything in the H264 and H265 standard. They use advanced filters to reduce the loss of image quality and also reduce the incidence of artifacts.
Differences H264 vs H265
The H265 standard is relatively new compared to the H264 of 18 years ago. Even so, perhaps due to compatibility, availability or popularity, the latter is still the most used by professionals in the area of video production and post-production.
When we evaluate the difference H264 vs H265 one of the things that comes out is the resolutions it can handle. MPEG-4 compresses high resolution formats, even larger than 4K, but the weight of the resulting file does not make it the best option. On the other hand, the HEVC compresses 4K videos as if it were child’s play up to 75% of the weight of the initial project in some cases. Even this type of technology could pave the way for the creation of new applications for the imminent entry of 8K video as the new default HDR format.
The segmentation algorithm
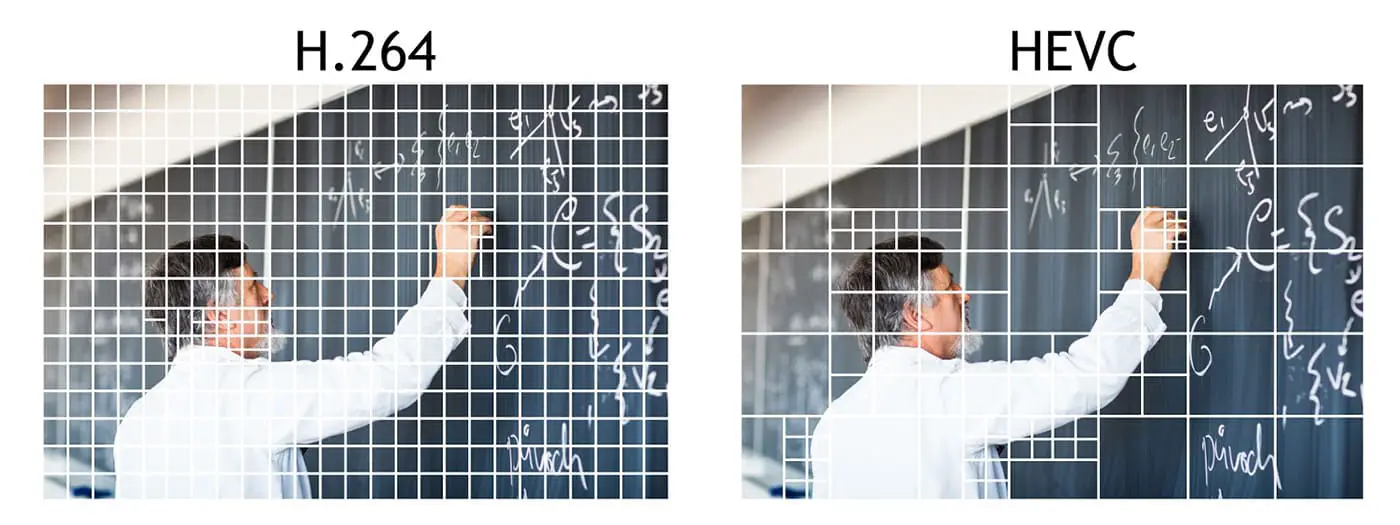

We already talked about the ability of these codecs to create a partition in a grid way to segment and optimize the processing of the images that make up the video. The H264 format is capable of slicing into 16 x 16 pixel chunks, also known as Macroblocks. From there, to improve the prediction process, it could be further partitioned into 4 x 4 pixel sections. The aspect ratio of these sections must always be square. Instead, the H265 format uses a segmentation system called CTU (Coding Tree Units) based on 64 x 64 pixels. Having a much larger base to work the partitions can be made in much smaller measures of 32 x 32, 16 x 16, 8 x 8 and 4 x 4. Also with this format you can have rectangles of 32 x 8, 8 x 32, 16 x 4, or 4 x 16.
The prediction algorithm in H265 consists of two basic processes for its operation: Interframe compression is when pixels are taken from adjacent frames to process the data from a more accurate data universe, and Intraframe compression, which is when it is taken the pixel information of the same frame to create these predictions. These two new processes help significantly to achieve significant compression levels. While the H264 standard only has 8 methods to process pixel data in the same frame, the H265 has 32 methods to do it with unsurpassed accuracy.
Natural vs Synthetic images
It is known like “natural” images those that show scenes of the daily life like direct photographies to surroundings or real people. On the other hand, “synthetic” images are all those that are generated or improved by the intervention of a computer, for instance, a render or animation from a 3D program. In a study it was determined that the reduction in the bitrate of the H265 codec in natural images can reach 50 to 74%, while in synthetic images it was consistent in 75%, without any perceptible trace of loss in quality from image.
New filtering processes
HEVC brings with it new processes to reduce artifacts in images caused by mosaicing of block segmentation: Sample Adaptive Offset and Adaptive Loop Filtering.The Sample Adaptive Offset proposes to eliminate the complexity of the video images by creating a spacing between each of the samples. Said spacing can be applied in two ways: through Band Offset or Edge Offset. On the other hand, Adaptive Loop Filtering proposes to reduce the mean square error through the use of Wiener-based adaptive filter.
The curse of processing
Although these video standards significantly reduce the weight of files, there is a whole background behind the playback process. The more compression required, the more computer processing required. With CPU and GPU increasingly powerful, more accessible and cheap, this does not seem to be a problem of major repercussions. The truth is that with the H264 codecs you still have the perfect balance with respect to the average processing.
In post-video production, rendering times depending on the amount of data we are processing can be considerably long. Rendering a video in H265 could take up to 10 times comparatively what a normal video in H264 would. This is due to the large number of calculations that the H265 algorithm requires to process.
Codec support
A major limitation and perhaps the main reason why the H265 standard has not yet caught on to the level that the H264 is is the support for video post-processing software. It will be a while before we see general support across the board for all video editing applications.
More stories like this
- H264 vs AV1 vs H265: What is the best video CODEC?
- How to connect two TVs together using a single source
- What are the most used output ports in modern video cards?
- How do I know if my computer can run 4K resolution
- Gigabyte Aorus FO48U gaming monitor full review
- How to know what is my screen resolution easily