You can also be interested in these:
- How to connect two TVs together using a single source
- How do I know if my computer can run 4K resolution
- Gigabyte Aorus FO48U gaming monitor full review
- How to know what is my screen resolution easily
The monitor or screen of a computer is the output peripheral par excellence, through it our PC communicates with us visually. The screen display is what makes the interaction with the digital interface possible, translating all those ceros and ones into actionable elements. In between these two elements there is one component responsible for delivering the signal to the output screen: The video output port. Let’s see what are the most used output ports in modern video cards, and also which ones are lagging behind in the time and technology development race.

Have you thought about why there are monitors and TVs? In these modern times both type of displays have almost the same amount of features and share even the same technologies, why don’t we call them both just monitors? There is a distinctive difference between monitors and televisions, which at the same time, turns out to be the reason both elements have developed technologically separately.
What is the difference between monitors and TVs video outputs?
The first computers used modified television screens. Their ability to receive radio signals was removed, and instead they fed the signal through cables. This happened due to the fact that in the middle of the Cold War, computer operators feared that the radio frequency systems could be intercepted for espionage purposes or accessed through radio communications used back then. This caused computer terminal displays to be sold without the ability to tune radio frequencies, but at the same time allowed the implementation of proprietary video input and output connectors.
Until the arrival of the PC AT in 1984, which brought the EGA standard, PC monitors were modified NTSC television screens, however, the limitations of this format when displaying images with higher definition created the need to adopt new formats of PC monitors with a horizontal frequency higher than NTSC 15.7KHz. At that point the path of televisions and monitors was separated by 20 years until the arrival of monitors and LCD televisions. Nonetheless, the difference remains the same, the lack of inclusion of a television tuner in the monitor.
We will embark on a journey through history to see the evolution of output connectors for monitors and, more into details, we will focus on those found on computer motherboards and video cards. There are a few types of video output ports that didn’t make it on this list, such as S-Video, Component, Composite, SCART and others, because are more likely to be used in television screens connections, and therefore, are out of the scope of this article.
Obsolete video output ports
Many of the connections featured in this section are still available in computers nowadays, however the only reason they are included is for backwards compatibility. They have fallen into a fast and generalized phase of disuse and will be soon discontinued. In other words, they have been replaced and they will not evolve, so if you find a monitor or a graphics card with this type of connectors, it is because is very old and it will not provide an acceptable performance matching today’s standard.

VGA port
Any PC from the 90s and the first half of the 2000s used VGA: a video connector of the RGB type. The way it worked is sending the information of the color components in three different channels, the connector also has the pins to control the horizontal and vertical synchronization of the monitor, which at that time was controlled by the graphics card itself. The synchronization pins indicate that it was a port designed for monitors that use a cathode ray tube to generate the image.
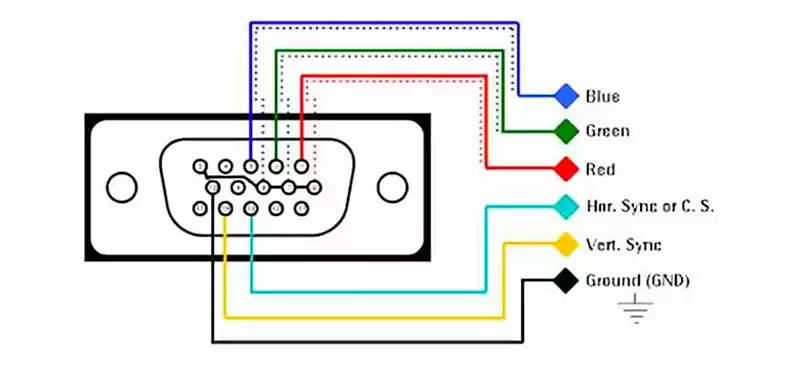
As it is a port for a PC monitor, it does not carry audio. This is because when the VGA first appeared on the PC, there was also an independent controller for the audio in form of an internal speaker or audio cards on the computer. By that time, there was no need to replace that entire sound system to be integrated in the monitor screen.
The VGA port carries an analog signal, which is almost the opposite modern LCD screens read as a video signal. In order to make these two signals compatible a new analog-to-digital converter interface had to be created. The degradation of the video signal was one of the key factors this signal conversion didn’t prosper.
DVI (Digital Video Interface) port
Time went by and LCD panels became cheaper, and users began to buy them due to the fact they allowed to save space on their desks compared to the classic tube monitors. However, as we learned from the story of the VGA port: New LCD monitors weren’t 100% compatible with the analog signal used by the VGA ports, and the interface they were using to convert it to digital wasn’t making things easier or better. Because of this, the DVI video port was created.
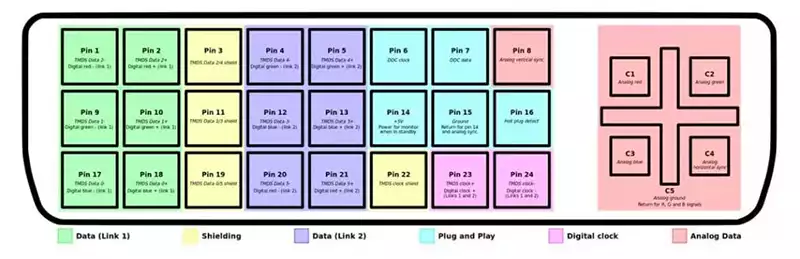
What are the differences between VGA and DVI? To begin with, DVI assigns two pins to each of the three RGB channels, although despite being a digital port it maintains the HSync and VSync pins, but they are hardly used. The DVI rendered synchronization pins obsolete because it had a series of pins from where the monitor sends the information about the resolution and the refresh rate, and this way the delivery of the signal is self-configured. The first ports that appeared in this category were the DVI-I, since they have the pins for use in analog monitors, however over time the DVI-D was standardized, which is intended purely for LCD screens as it lacks the pins for the CRT screens.
There were two different generations of the DVI video connector. On one hand the SL with a maximum resolution of 1920 x 1200 pixels and on the other the DL with a resolution of 2560 x 1600 pixels, also at 60 Hz. On the downside, the DVI never supported variable frequency rates and over time it was quickly replaced by HDMI and DisplayPort.
Video outputs in use today
The video output ports we are going to mention in this section are those we can find in modern graphics cards and PC monitors. The fact that the panels are the same in both flat screen televisions and monitors has completely universalized the video interfaces and with it the different connectors. Nowadays, it is quite common to see a computer setup with a television as an output screen, however, monitors will be always ahead of the game when it comes to quality and performance. Let’s say the benefit of televisions is having a bigger size display for less money.

HDMI port
The most widely used video output port today and with almost twenty years of evolution, it has gone from displaying images at 720p in its 1.0 version to 8K resolutions with 2.1, which represents an increase of 50 times more pixels than its origin. In its evolution we have seen additions such as support for various aspect ratios, variable frequency rate, HDR, and so on.
The HDMI port was born as a variant of the DVI port, but it represented an abysmal leap in advancements, especially in its design and shape, as well as the distribution of the pins. The differences with DVI? Since it was created as a video output for audiovisual content, it can carry audio and also contains video for HDCP, the content protection system still used today by the audiovisual industry.
The HDMI cable is designed to deliver signal without losses with an standard distance of up to 5 meters, a much greater distance between the target and source devices, without any losses in the quality of the signal. However, it is important to keep the computer as close as possible to the monitor if such a video connector is used. On the downside, the HDMI standard is really susceptible to cable length. Going further than 10 feet in cable length will cause signal issues and screen flickering.
DisplayPort or DP
One of the most used video output ports in monitors and PC graphics cards. DisplayPort, just like HDMI, has had several different generations in its evolution until today. The big difference is that they were born from two different standardization committees and that is why DisplayPort is seen more on monitors than on televisions. Moreover, many times a good way to know if a screen is a television or a monitor is the inclusion of this port, although we see more and more TV manufacturers adopting this technology every day.
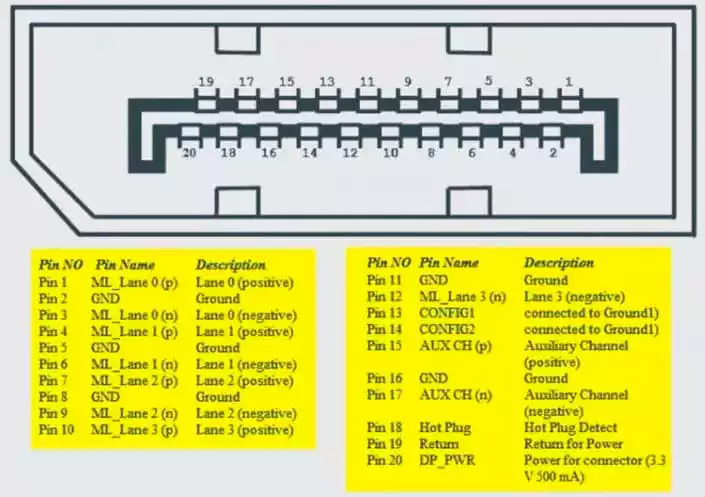
The big difference between HDMI and DisplayPort apart from their shape and pin distributions is that HDCP support for certain content is not mandatory in a DP interface, this means that for video game consoles and video players this type of connector It is not used, as this medium is essential for the reproduction of commercial audiovisual content. That is why the DisplayPort represents the future of the video output ports. Just like the HDMI, DisplayPort has the ability to transmit audio.
DisplayPort over USB
The USB-C port has come to revolutionize the computer connectivity in general, including the video output ports. It uses its enormous bandwidth to transmit the video signal, at the same time that it is used to transmit data through the USB 2.0 pins and serve also to power the monitor. It may become the most used port in the future by allowing the screen to take advantage of the power supply adapter and make them totally portable, of course, this will require that the bandwidth exceed HDMI 2.1, which we can see already available with Thunderbolt-based USB 4.0.
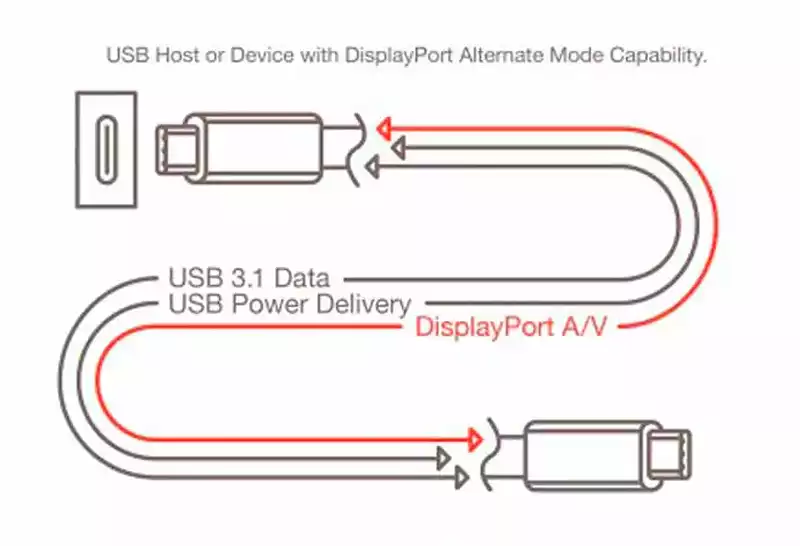
At the moment not everybody is using it. Only time will tell if they become as widely used and accessible as HDMI once was. For many, the DisplayPort technology is closer to extinction than HDMI, because all the monitors that still uses HDMI until now, but DP is being threaded to be replaced by USB-C ports with the ability to transmit video.
More stories like this
- How to connect two TVs together using a single source
- How do I know if my computer can run 4K resolution
- Gigabyte Aorus FO48U gaming monitor full review
- How to know what is my screen resolution easily
- What are the best monitors with HDMI 2.1 support?
- H264 vs AV1 vs H265: What is the best video CODEC?
