You can also be interested in these:
- Where does the CPU store its computations?
- Everything about the DDR5 RAM technology
- Cache vs RAM memory: How much should my computer have?
- How to change memory frequency in BIOS Asus?
You have surely heard of the term DIMM on more than one occasion, or you may have read it in some of the characteristics of motherboards, RAM memories, etc. This format is important when making an expansion of the main memory or when buying the module for your PC configuration, since it is what determines whether it is compatible with the slot or slot on the motherboard.
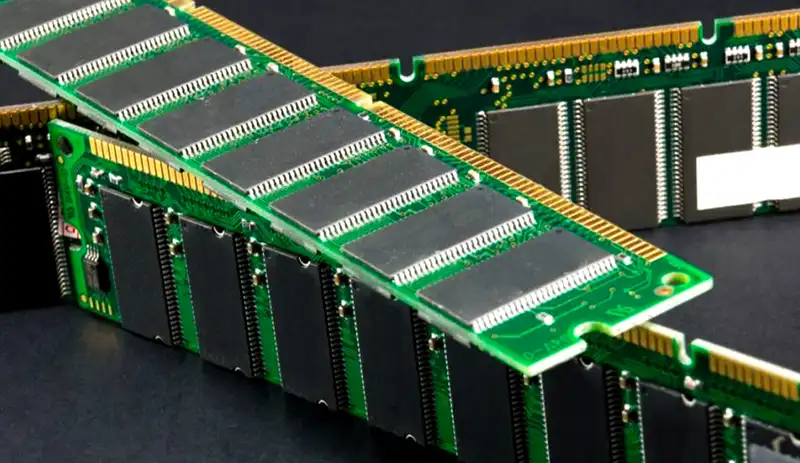
For these reasons, you should know what DIMM is and what cases it is used for, as well as its types, and existing alternatives.
What is a DIMM?
RAM memory comes in module format, and current modules are of the DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) type, or two-line module. These modules come with two rows or sides of memory chips and plug into a single slot. In addition, they include a groove on the connectors so that the connection can only be made in one way, respecting the pinout and polarity.
Before DIMMs came:
- SIPP (Single In-line Pin Package): it was a simple package, with in-line memory chips and pins to insert into a socket on the motherboard. They were used on the 80286 and contemporaries.
- SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module): These were introduced as the replacements for SIPPs and were popular from the early 1980s to the 1990s. Unlike DIMMs, they only use chips on one lane of the module, and unlike SIPPs, they don’t use pins, but rather connection pads for the slot.
- RIMM (for the Rambus): similar to the SIMM, with two faces, it was a type of format specially designed for the Rambus memories that became popular in the 90s, and that ended up disappearing with the arrival of DDR technology, cheaper and with similar benefits.
There were some other memory attempts like the invention of iRAM by Gigabyte. A memory that was inserted into slots on a PCI card and was intended to act like a conventional hard drive, but much faster. The idea was to use this expansion card with DIMM slots to be able to insert any type of conventional RAM module, acting as a form of ultra-fast secondary storage. Despite that, this development did not have the expected reception, and has finally been replaced by SSDs.
DIMM types
Within the DIMM-type modules we find variants in terms of the number of pins according to the DDR SDRAM memory they mount. The number of contacts of each of these types is:
- 168-pin DIMM for SDR-SDRAM
- 184-pin DIMM for DDR SDRAM
- 240-pin DIMM for DDR2-SDRAM and also for DDR3
- 288-pin DIMM for DDR4 and DDR5 SDRAM
The DIMM notch is also located at a different point on the edge of the contacts on each of these types. These modules also have notches on the sides that are for the anchors of the base plate, so that the modules are kept in their position.
SO-DIMM: Differences
For laptop computers, a different DIMM module has been developed, with a smaller size. It is known as SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM). These modules hide some differences with respect to their older brothers, and they go beyond size, since they are shorter. They also sit parallel to the motherboard, since there isn’t as much space to sit them perpendicular as DIMMs.
The objectives for which SO-DIMM was created are summarized in four fundamental points:
- Reduce the size of the module so that the slot does not require as much motherboard surface area on laptops.
- Lower power consumption to make the batteries last longer autonomy.
- Reduce the number of connectors through which heat is also transmitted.
- Clear the path through which the air circulates in the cooling system of this equipment.
- Possibility to solder the memory to the motherboard.
The alternative most feared by users
LPDDR memories, such as the low-power versions for ultra-compact mobile and portable devices, are usually soldered to the motherboard. Something that everyone wants to avoid at all costs when they buy a laptop, since there are modular alternatives to be able to replace the RAM in case it fails, or to expand the memory if needed.
However, those that are welded cannot be extended, nor can they be replaced if they are damaged. They could be removed in a specialized workshop and replaced with another functional part. But, sometimes, this can be more expensive, and detrimental to the rest of the PCB elements since they are subjected to high temperatures to remove the unusable chips and solder the new ones (reballing). Only some equipment models allow you to expand the memory with an additional SO-DIMM slot, but it is still not possible to easily replace the one that is integrated.
More stories like this
- Where does the CPU store its computations?
- Everything about the DDR5 RAM technology
- Cache vs RAM memory: How much should my computer have?
- How to change memory frequency in BIOS Asus?
- How to allocate more RAM to a game for improved performance
- Corsair Dominator Platinum RGB DDR5 review
